Fundamentals of Orthopedic Physical Therapy
Orthopedic physical therapy is guided by several foundational principles:
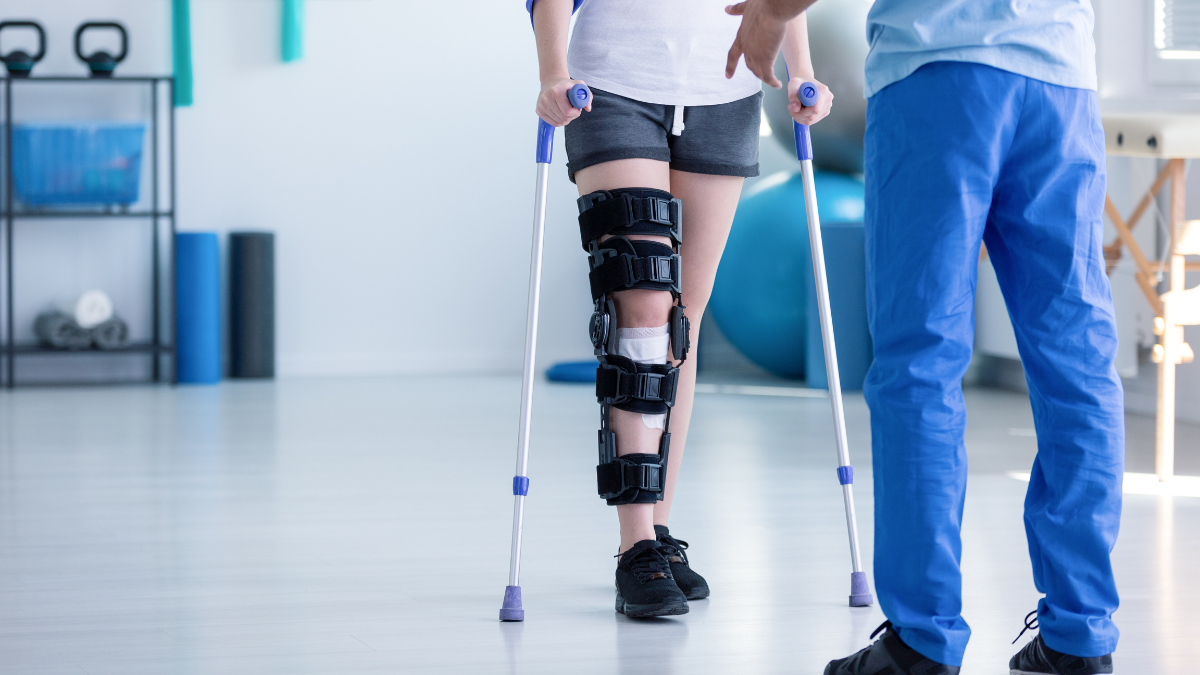
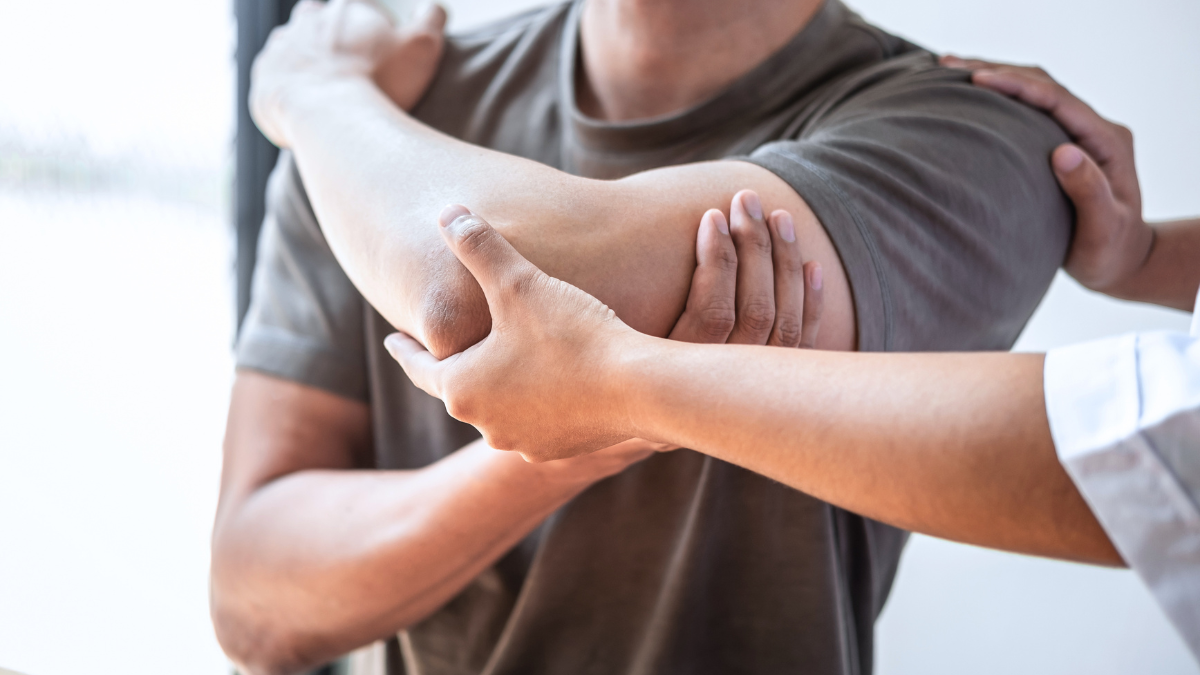
Manual Therapy: This includes joint mobilization and soft tissue manipulation to reduce pain, improve circulation, and enhance mobility.
Exercise Prescription: Specific exercises tailored to improve strength, flexibility, balance, and coordination.
Modalities: These include heat, cold, ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and laser therapy, designed to reduce pain and inflammation, promote healing, and accelerate recovery.
Patient Education: Educating patients on proper posture, body mechanics, and self-care techniques is vital to prevent further injury and ensure long-term recovery.
